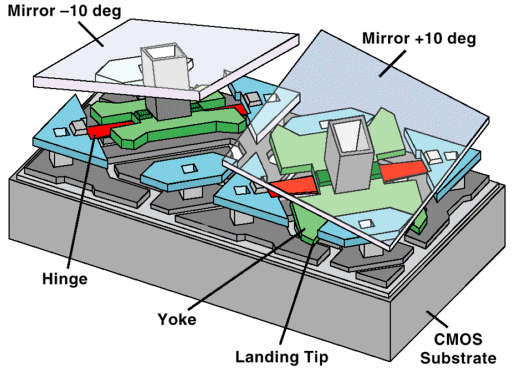
Digital Micromirror Devices (DMDs)
(aka Digital Light Processing / DLP / commercial name)
(A Micro-Optical Electromechanical Device - MOEMS - for Display Applications)
|
|
|
|
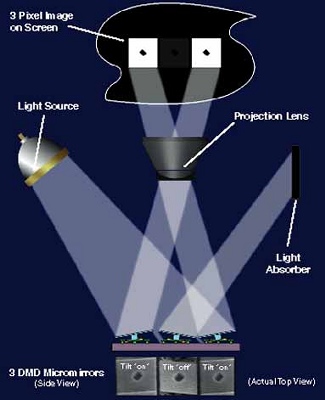
Three Mirrors Project Image Incoming light hits the three mirror pixels. The two outer mirrors that are turned on reflect the light through the projection lens and onto the screen. These two "on" mirrors produce square, white pixel images. The central mirror is tilted to the "off" position. This mirror reflects light away from the projection lens to a light absorber so no light reaches the screen at that particular pixel, producing a square, dark pixel image. In the same way, the remaining mirror pixels reflect light to the screen or away from it. By using a color filter system and by varying the amount of time each of the DMD™ mirror pixels is on, a full-color, digital picture is projected onto the screen. |
|
|
|
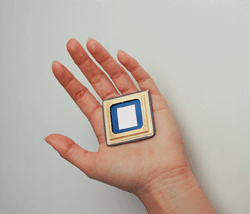 SXGA DMD on Hand SXGA device with black aperture: 1280x1024; 1,310,720 mirrors |
|
Digital Micromirror Device: an array of semiconductor-based digital mirrors that precisely reflect a light source for projection display and hard-copy applications. A DMD enables Digital Light Processing and displays images digitally. Rather than displaying digital broadcast signals as analogue signals, a DMD directs the digital signal directly to your screen.