Packet Switching
Phone network : provide a dedicated, switched path to the caller and the receiver for the duration of the call
internets : Messages are divided into relatively small blocks of data, commonly referred to as packets.
Routing : a way to send each packet at the right address
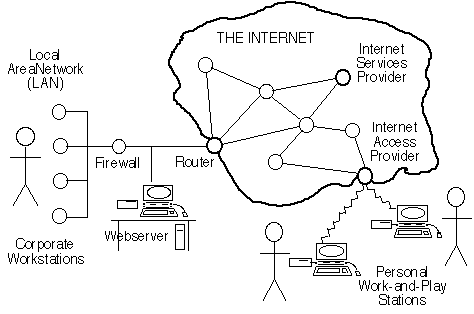
The networks that had been designed to
support voice-conversations provided a dedicated, switched path to the caller
and the callee for the duration of the call, and then released all of the
segments for use by other callers. Data networks were designed to apply a
very different principle. Messages were divided into relatively small blocks
of data, commonly referred to as packets. Packets despatched
by many senders were then interleaved, enabling efficient use of a single
infrastructure by many people at the same time. This is referred to as a packet-switched
network, in comparison with the telephony PSTN, which is a circuit-switched
network. The functioning of a packet-switched network can be explained using
the metaphor of a postal system (Clarke 1998).
http://www.anu.edu.au/people/Roger.Clarke/II/OzI04.html