Blinn & Torrance Variation
Jim Blinn introduced another approach for computing Phong-like illumination based on the work of Ken Torrance.
His illumination function uses the following equation:
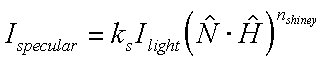
In this equation the angle of specular dispersion is computed by how far the surface's normal is from a vector bisecting the incoming light direction and the viewing direction.
 |
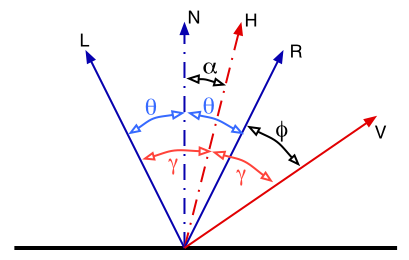 |
q + f = a + g q + a = g => f - a = a
f = 2a
On your own you should consider how this approach and the previous one differ.
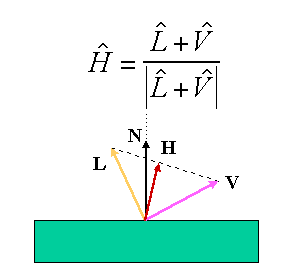
N : Normal to the real plan
H : Normal to the plane that would create higher reflexion towards the viewer
Advantage : the angle (N,H) will always remains between 0 and PI/2
Careful : nshiny should introduce a factor 2 with the previous expression.